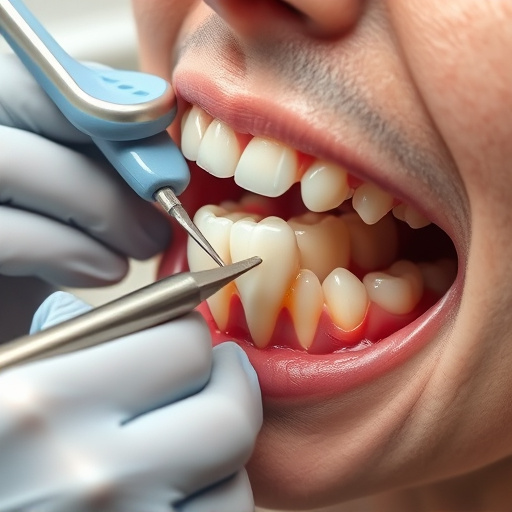
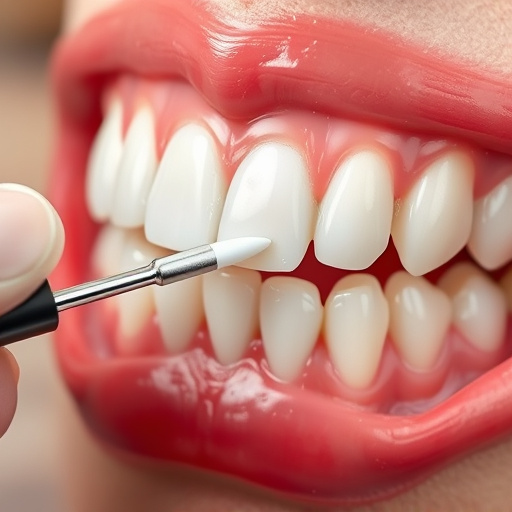
Dental sealants for teeth act as protective barriers, filling grooves and pits on molars and premolars to prevent plaque buildup and tooth decay. These clear coatings inhibit bacteria adhesion, creating a smooth surface that toothbrush bristles can't reach. Commonly used in children, adults can also benefit post-wisdom tooth removal or dental cleanings, reducing future restorative needs and extending teeth life. Applied as a liquid resin, sealants offer an effective, cost-efficient alternative to procedures like wisdom tooth extraction, making them ideal for maintaining oral health and avoiding future dental expenses.
Dental sealants for teeth are an effective protective measure against decay, acting as a barrier on the tooth surface. This article delves into the science behind these clear coatings, explaining how they prevent tooth decay by sealing off spaces where bacteria can collect. By understanding the application process and its benefits, you’ll grasp why dental sealants are a smart choice for maintaining oral health, especially in children but also for adults at risk of cavities.
- Understanding Dental Sealants: A Protective Barrier
- How Dental Sealants Prevent Tooth Decay
- Benefits and Considerations for Sealant Application
Understanding Dental Sealants: A Protective Barrier

Dental sealants for teeth act as a protective barrier, filling in the deep grooves and pits on our molars and premolars where plaque and food debris can easily get trapped. These clear or white coatings are applied to the chewing surfaces of back teeth, creating a smooth, glossy surface that prevents bacteria from adhering. By sealing these crevices, dental sealants significantly reduce the risk of tooth decay, especially in areas that are difficult for toothbrushes and floss to reach.
While they might be most commonly associated with children, dental sealants can also benefit adults, even those who have undergone procedures like wisdom tooth removal or regular dental cleanings. By providing an extra layer of defense against cavities, sealants can extend the life of teeth and reduce the need for future restorative treatments.
How Dental Sealants Prevent Tooth Decay
Dental sealants for teeth act as a protective barrier against decay-causing bacteria and acids. When applied to the chewing surfaces of back teeth, sealants create a smooth, hard coating that blocks food particles and plaque from settling in tiny crevices and pits where toothbrush bristles can’t reach. This prevents the formation of cavities and tooth decay, especially in areas prone to tartar buildup.
Unlike other dental procedures like wisdom tooth removal or needing clear aligners for invisibility, sealants offer a non-invasive solution. They are typically applied as a liquid resin that hardens quickly, providing long-lasting protection. Dental implants, while effective for some, require more extensive treatment and aren’t always necessary for preventing decay in the first place. Sealants can be a smart preventive measure, particularly for children and teenagers, to maintain oral health and avoid costly dental procedures later on.
Benefits and Considerations for Sealant Application
Dental sealants for teeth offer a powerful preventive measure against tooth decay, especially for children and young adults. These protective coatings are applied to the chewing surfaces of back teeth, creating a barrier that prevents food particles and bacteria from settling in hard-to-reach areas. By sealing off these crevices, dental sealants significantly reduce the risk of cavities forming.
When considering sealant application, both general and restorative dentistry practices play vital roles. General dentistry provides an ideal setting for initial assessments and routine applications, targeting primary teeth. Restorative dentistry, on the other hand, can address specific decay concerns in older patients by applying sealants as a complementary treatment to fillings or other restorations, enhancing overall oral health and longevity.
Dental sealants for teeth offer a simple yet effective shield against decay, acting as a protective barrier on the chewing surfaces of back teeth. By sealing out food particles and bacteria, these sealants reduce the risk of cavities and promote oral health. Understanding their application and benefits can help parents make informed decisions to protect their children’s teeth or individuals take proactive measures for their own dental well-being.